2023年12月7日,来自美国纪念斯隆-凯特琳癌症中心Michael G. Kharas研究组在学术期刊《细胞-干细胞》发表了标题为“SON is an essential m6A target for hematopoietic stem cell fate.”的研究成果,发现SON是影响造血干细胞命运的重要m6A靶点。
据悉,干细胞通过对称和非对称分裂来调节自我更新和分化命运决定。RNA m6A甲基化通过未知机制控制造血干细胞对称分裂和炎症。
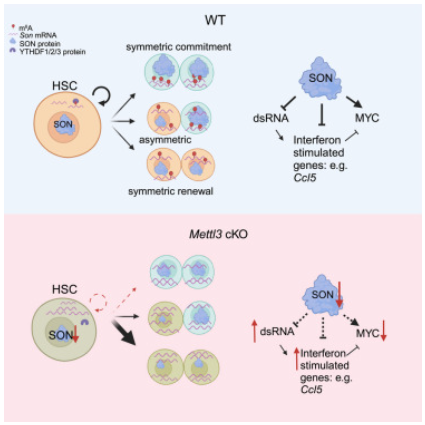
研究人员证明核斑点蛋白SON是小鼠造血干细胞自我更新、对称分裂和炎症控制所必需的m6A靶点。对m6A的全局分析发现,在造血干细胞分裂过程中,Son mRNA的m6A甲基化增加。当m6A缺失时,Son mRNA增加,但其蛋白会耗竭。重新表达SON可挽救造血干细胞对称分裂和移植缺陷。相反,Son缺失则会导致造血干细胞功能丧失,而过表达SON通过增加静止期来改善小鼠和人造血干细胞的移植潜力。
从机理上讲,SON能挽救MYC并通过转录调控抑制METTL3-造血干细胞炎症基因表达程序,包括CCL5。因此,该研究结果确定了控制炎症和造血干细胞命运的m6A-SON-CCL5通路。
Highlights
- •DART-seq identified SON as an m6A target critical for HSC commitment
- •SON rescues m6A HSC defect and is asymmetrically segregated during HSC division
- •SON enhances mouse and human HSC function
- •The m6A-SON-CCL5 axis controls HSC inflammation and fate
Summary
Stem cells regulate their self-renewal and differentiation fate outcomes through both symmetric and asymmetric divisions. m6A RNA methylation controls symmetric commitment and inflammation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) through unknown mechanisms. Here, we demonstrate that the nuclear speckle protein SON is an essential m6A target required for murine HSC self-renewal, symmetric commitment, and inflammation control. Global profiling of m6A identified that m6A mRNA methylation of Son increases during HSC commitment. Upon m6A depletion, Son mRNA increases, but its protein is depleted. Reintroduction of SON rescues defects in HSC symmetric commitment divisions and engraftment. Conversely, Son deletion results in a loss of HSC fitness, while overexpression of SON improves mouse and human HSC engraftment potential by increasing quiescence. Mechanistically, we found that SON rescues MYC and suppresses the METTL3-HSC inflammatory gene expression program, including CCL5, through transcriptional regulation. Thus, our findings define a m6A-SON-CCL5 axis that controls inflammation and HSC fate.
文章来源:
Hanzhi Luo, Mariela Cortés-López, Cyrus L. Tam et al, SON is an essential m6A target for hematopoietic stem cell fate.DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.11.006,Cell Stem Cell:最新IF:25.269







