2024年6月26日,来自武汉大学殷昊团队在Cell 在线发表题为“Amplification editing enables efficient and precise duplication of DNA from short sequence to megabase and chromosomal scale”的研究论文,该研究开发了一种名为扩增编辑(AE)的基因组编辑工具,可以在染色体尺度上精确地进行可编程DNA复制。AE可以复制20 BP到100 Mb的人类基因组,大小与人类染色体相当。
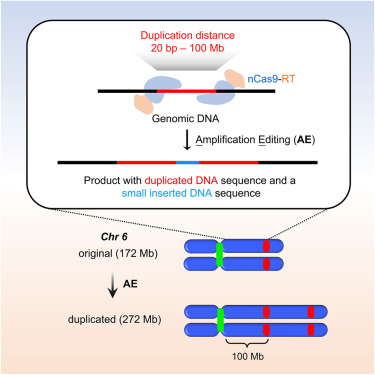
研究开发了一种名为扩增编辑(AE)的方法,以可编程的方式精确有效地复制基因组序列从20 bp到100 Mb。由于复制大小从20 bp到约8 kb不等,AE可以多次复制以生成多个副本。AE复制1 Mb的效率为73.0%,复制100 Mb的能力达到染色体尺度(人类14号染色体的大小为107 Mb)。通过AE复制100 Mb,该研究观察到染色体的表型延伸和长臂上标记基因的重复。复制是精确的,全基因组测序和连接的深度测序证明了这一点。AE是一种能够高效、精确地设计染色体结构的基因组编辑工具,将精确基因组编辑的版图从单个基因座扩展到染色体尺度。
Highlights
•AE achieves duplication of 20 bp to 100 Mb with high efficiency and precision
•AE generates multiple repeats with duplication ranging from 20 bp to 8 kb
•Mb-level duplications have been realized in embryonic stem cells and primary cells
•AE treatment can upregulate expressions of non-coding RNA and a coding gene
Summary
Duplication is a foundation of molecular evolution and a driver of genomic and complex diseases. Here, we develop a genome editing tool named Amplification Editing (AE) that enables programmable DNA duplication with precision at chromosomal scale. AE can duplicate human genomes ranging from 20 bp to 100 Mb, a size comparable to human chromosomes. AE exhibits activity across various cell types, encompassing diploid, haploid, and primary cells. AE exhibited up to 73.0% efficiency for 1 Mb and 3.4% for 100 Mb duplications, respectively. Whole-genome sequencing and deep sequencing of the junctions of edited sequences confirm the precision of duplication. AE can create chromosomal microduplications within disease-relevant regions in embryonic stem cells, indicating its potential for generating cellular and animal models. AE is a precise and efficient tool for chromosomal engineering and DNA duplication, broadening the landscape of precision genome editing from an individual genetic locus to the chromosomal scale.
文章来源:
Ruiwen Zhang,Zhou He ,Yajing Shi et al, Amplification editing enables efficient and precise duplication of DNA from short sequence to megabase and chromosomal scale. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2024.05.056 Cell