2024年11月26日,来自澳大利亚新南威尔士大学Stuart G. Tangye等研究人员合作在《免疫》杂志发表了标题为”Impaired development of memory B cells and antibody responses in humans and mice deficient in PD-1 signaling.“的研究成果,发现PD-1信号缺失的小鼠和人类中记忆B细胞和抗体反应的发育受损。
研究人员表示,T滤泡辅助(Tfh)细胞大量表达免疫受体程序性细胞死亡蛋白1(PD-1),且PD-1缺失对小鼠抗体(Ab)介导免疫的影响与Tfh细胞功能的损害相关。
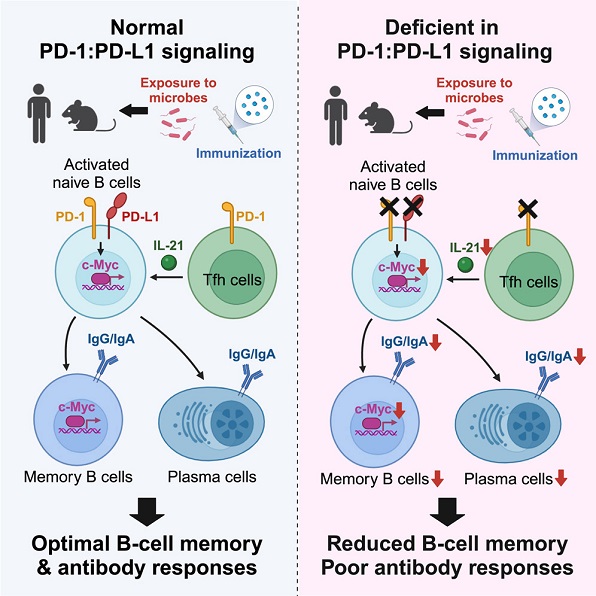
研究示意图
研究人员重新探讨了PD-1-PD-L1轴在抗体介导免疫中的作用。具有遗传性PD-1或PD-L1缺失的个体具有较少的记忆B细胞和受损的抗体反应,类似于Pdcd1−/−和Cd274−/−Pdcd1lg2−/−小鼠。PD-1、PD-L1或两者均可在体外激活后的人类初始B细胞表面被检测到。
缺失PD-1或PD-L1的B细胞在体内表现出转录调控因子c-Myc及其靶基因的表达减少,且PD-1缺失或中和PD-1或PD-L1抑制了人类B细胞中c-Myc的表达和抗体产生。此外,B细胞特异性删除Pdcd1可防止小鼠中记忆B细胞的生理积累。
因此,PD-1通过B细胞内在和外在机制,塑造了最佳的B细胞记忆和抗体介导免疫,这提示B细胞的失调可能在抗PD-1-PD-L1免疫疗法后,引发感染性和自身免疫并发症。
Highlights
•Impaired B cell memory in PD-1- and PD-L1-deficient humans and mice deficient in PD-1 signaling
•PD-1 deficiency but not PD-L1 deficiency disrupts Tfh cell phenotype and function
•Human PD-1-PD-L1 axis promotes antibody responses in a B cell-intrinsic manner
•B cell-specific deletion of PD-1 triggers striking phenotypic alterations in mice
Summary
T follicular helper (Tfh) cells abundantly express the immunoreceptor programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), and the impact of PD-1 deficiency on antibody (Ab)-mediated immunity in mice is associated with compromised Tfh cell functions. Here, we revisited the role of the PD-1-PD-L1 axis on Ab-mediated immunity. Individuals with inherited PD-1 or PD-L1 deficiency had fewer memory B cells and impaired Ab responses, similar to Pdcd1−/− and Cd274−/−Pdcd1lg2−/− mice. PD-1, PD-L1, or both could be detected on the surface of human naive B cells following in vitro activation. PD-1- or PD-L1-deficient B cells had reduced expression of the transcriptional regulator c-Myc and c-Myc-target genes in vivo, and PD-1 deficiency or neutralization of PD-1 or PD-L1 impeded c-Myc expression and Ab production in human B cells isolated in vitro. Furthermore, B cell-specific deletion of Pdcd1 prevented the physiological accumulation of memory B cells in mice. Thus, PD-1 shapes optimal B cell memory and Ab-mediated immunity through B cell-intrinsic and B cell-extrinsic mechanisms, suggesting that B cell dysregulation contributes to infectious and autoimmune complications following anti-PD-1-PD-L1 immunotherapy.
文章来源:
Masato Ogishi, Koji Kitaoka et al, Impaired development of memory B cells and antibody responses in humans and mice deficient in PD-1 signaling.DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.10.014, 最新IF:43.474







